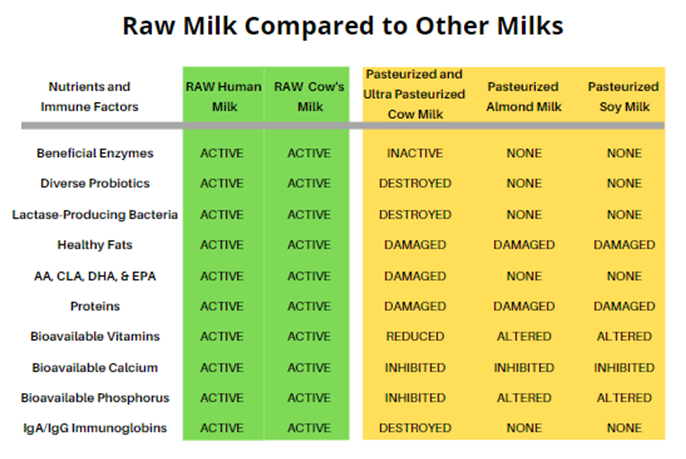
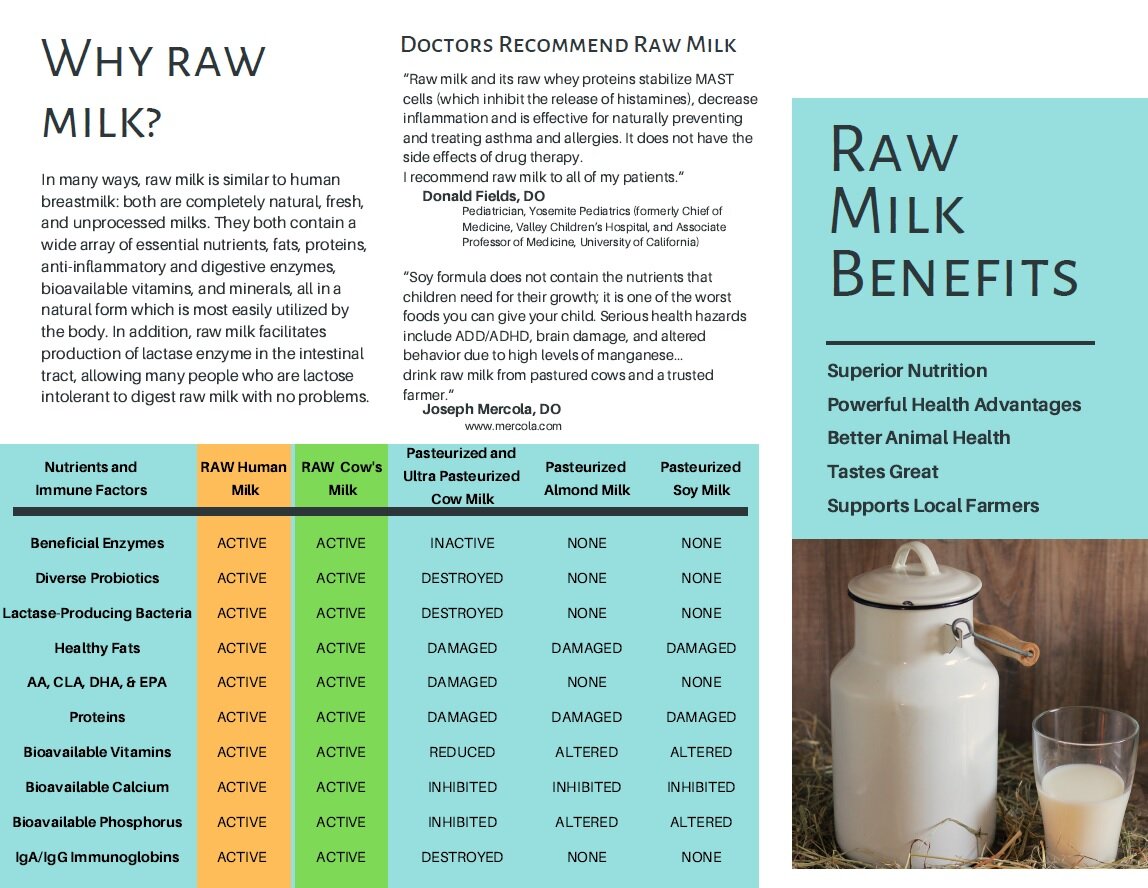
Back in 2011 before the Raw Milk Institute (RAWMI) was formed, there were no universal standards for safe raw milk production. Consumer demand for raw milk was expanding, as people learned about the health benefits of raw milk as well as the negative effects of pasteurization. There was a growing body of evidence that children who drink raw milk have decreased rates of asthma, allergies, eczema, ear infections, fever, and respiratory infections. Whereas pasteurized milk is a top food allergen and difficult to digest, raw milk is actually a health-supporting food with rich therapeutic potential that is easily digested by most consumers. Yet, standards for raw milk varied widely from state to state and country to country.
The occasional foodborne illness outbreaks that could be tied to raw milk continued to tarnish raw milk’s reputation. And worse yet, some of these outbreaks actually led to life-threatening illnesses. As raw milk’s popularity grew, it was being consumed by a wider segment of the population including immune-compromised people. Whereas average healthy people are likely to have relatively mild symptoms from exposure to foodborne pathogens, immune-compromised people are more likely to have severe symptoms.
Perfectly Safe Food?
It is important to note that there is no such thing as a perfectly safe food. A CDC analysis of foodborne illnesses from 2009-2015 showed that the top food categories commonly linked to illnesses were chicken, pork, and seeded vegetables. Multi-state foodborne illness outbreaks have been linked to foods ranging from unpasteurized apple juice to ground beef to soy nut butter to lettuce.
Pasteurized milk is not perfectly safe, either, and is implicated in foodborne illnesses and outbreaks every year. Although a wide range of foods including meats and vegetables are known to have the potential for causing foodborne illnesses, only raw milk is targeted by government regulators as a food to be completely avoided. Countries such as Canada and Australia currently have complete bans on raw milk.
Raw Milk Institute Method for Safe Raw Milk
The Raw Milk Institute was founded in 2011 to advance the cause of safe raw milk. The numerous health benefits of raw milk make it an essential food, which is too important to be allowed to be systematically suppressed by regulators and government agencies. RAWMI sought to better understand the important factors in ensuring that raw milk was safe to consume.
In 2011-12, RAWMI brought together a diverse international group with the purpose of establishing standards for safe raw milk. This group included medical doctors and epidemiologists, nutritional consultants, veterinarians, food safety scientists, raw milk farmers, and raw milk consumers. This collaborative group developed the Raw Milk Institute Common Standards, which were initially released in 2012.
The RAWMI Common Standards describe a three-pronged approach for the production of safe raw milk which consists of:
Farmer training and mentoring
Risk Analysis and Management Plan (RAMP) for the unique conditions on each individual farm
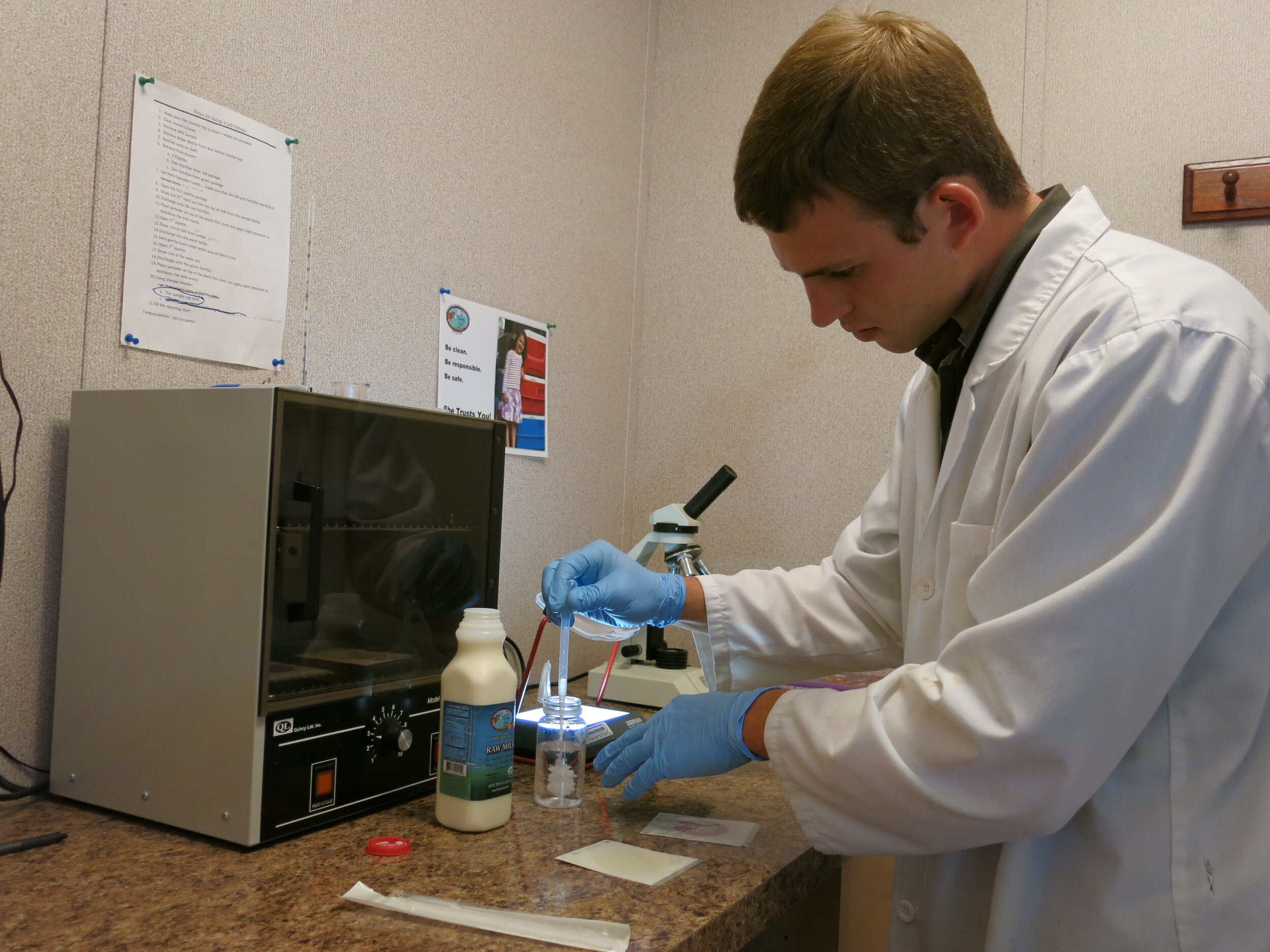
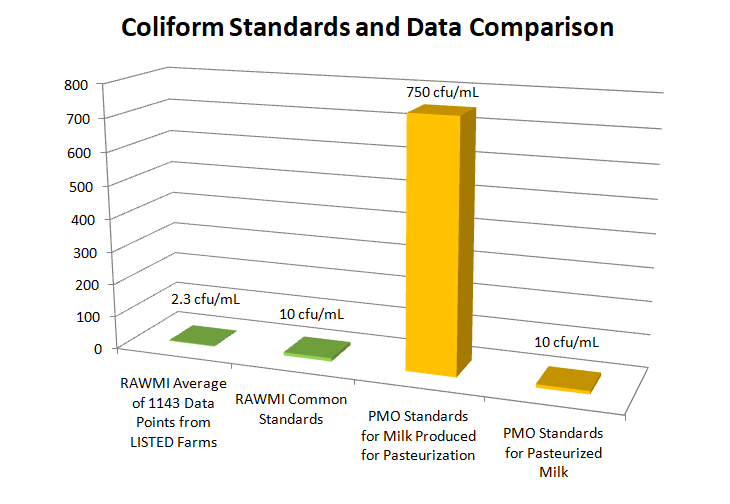
Stringent yet achievable bacterial test standards for coliforms and Standard Plate Count (SPC)
The Common Standards Work!
Since their release in 2012, the RAWMI Common Standards have become a foundational part of low-risk raw milk production across North America. When farmers are well-trained, use careful production practices as laid out in their individual RAMP, and perform ongoing bacterial testing of their milk, they can produce raw milk that is ultra-low-risk.
Researchers from Canada and Europe have studied the safety of raw milk intended for direct human consumption, and have specifically considered milk from farms who implement the RAWMI Common Standards. They have found that carefully produced raw milk is a low-risk food which is fundamentally different from pre-pasteurized milk. The implementation of the RAWMI Common Standards has led to a significant reduction in raw milk-related illnesses and outbreaks.
The table below contrasts pathogen test data from pre-pasteurized milk vs. raw milk intended for direct human consumption. As illustrated in the table, pathogen testing of pre-pasteurized milk samples has detected pathogens in up to 33% of samples. In contrast, there were zero pathogens detected in thousands of milk samples from raw milk intended for direct human consumption. It is clear from this test data that pre-pasteurized milk is categorically different from raw milk intended for direct human consumption.
Data courtesy British Columbia Herdshare Association
Common Standards and RAMP 2020 Update
Knowledge about safe raw milk is continually advancing. With the review of the RAWMI Advisory Board and LISTED farmers, the RAWMI Common Standards and RAMP have recently been updated to include the latest information about best practices in raw milk production. The updated Common Standards and RAMP are also now inclusive of other dairy animals such as goats and sheep. The 2020 Common Standards and RAMP are available here: